ComputerComputer FieldsMain |
Networking What is networking ?In the world of computers, networking is the practice of linking two or more computing devices together for the purpose of sharing data. Networks are built with a mix of computer hardware and computer software. Area NetworkNetworks can be categorized in several different ways. One approach defines the type of network according to the geographic area it spans. Local area networks (LANs), for example, typically span a single home, school, or small office building, whereas wide area networks (WANs), reach across cities, states, or even across the world. The Internet is the world's largest public WAN. Networking types:One way to categorize the different types of computer network designs is by their scope or scale. For historical reasons, the networking industry refers to nearly every type of design as some kind of area network.Common examples of area network types are:
LAN and WAN were the original categories of area networks, while the others have gradually emerged over many years of technology evolution. Network topology:The physical topology of a network refers to the configuration of cables, computers, and other peripherals. Physical topology should not be confused with logical topology which is the method used to pass information between workstations. Logical topology was discussed in the Protocol chapter. Main Types of Physical Topologies:The following sections discuss the physical topologies used in networks and other related topics.
Linear busA linear bus topology consists of a main run of cable with a terminator at each end (See fig. 1). All nodes (file server, workstations, and peripherals) are connected to the linear cable. 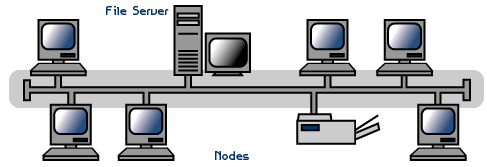
Advantages of a Linear Bus Topology
Disadvantages of a Linear Bus Topology
Star TopologyAlternatively referred to as a star bus topology, tree topology is one of the most common network setups that is similar to a bus topology and a star topology. A tree topology connects multiple star networks to other star networks. Below is a visual example of a simple computer setup on a network using the star topology. 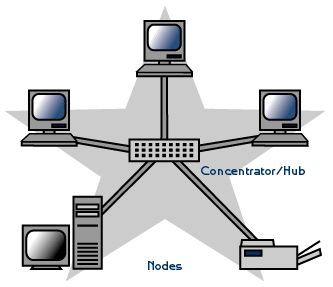
Tree TopologyTree Topology integrates the characteristics of Star and Bus Topology. Earlier we saw how in Physical Star network Topology, computers (nodes) are connected by each other through central hub. And we also saw in Bus Topology, work station devices are connected by the common cable called Bus. After understanding these two network configurations, we can understand tree topology better. In Tree Topology, the number of Star networks are connected using Bus. This main cable seems like a main stem of a tree, and other star networks as the branches. It is also called Expanded Star Topology. Ethernet protocol is commonly used in this type of topology. 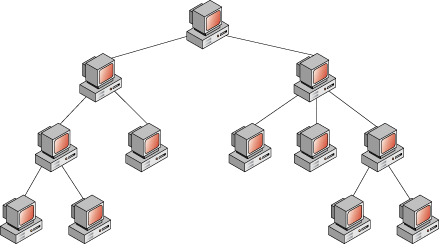
Ring TopologyAlternatively referred to as a ring network, the ring topology is a computer network configuration where each network computer and device are connected to each other forming a large circle (or similar shape). Each packet is sent around the ring until it reaches its final destination. Today, the ring topology is seldom used. Below is a visual example of a simple computer setup on a network using a ring topology. 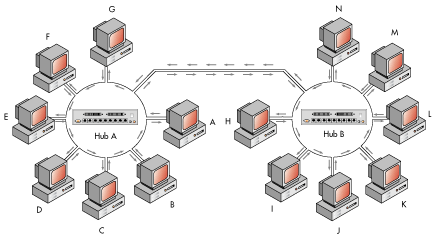
Mesh TopologyA network setup where each computer and network device is interconnected with one another, allowing for most transmissions to be distributed, even if one of the connections go down. This topology is not commonly used for most computer networks as it is difficult and expensive to have redundant connection to every computer. However, this topology is commonly used for wireless networks. Below is a visual example of a simple computer setup on a network using a mesh topology. 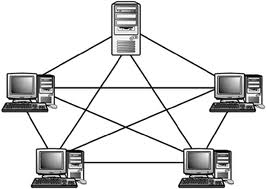
|